- Dividend investing is a method of generating growing passive income. It also reduces portfolio volatility. On average, dividend stocks perform better than growth stocks during crises.
- There are two investment strategies aimed at generating dividend income. The first is buying individual shares, and the second is investing in dividend ETFs.
- Dividend yield is one of the criteria used to select stocks for a dividend portfolio. However, it cannot be the only one. High-dividend stocks often have unreliable payouts.
In this article, we will discuss the largest dividend stocks and explain what you need to study before deciding to invest in dividend stocks.
Table of Contents
Understanding Dividend Stocks and Their Benefits
Dividend stocks are shares in companies that regularly distribute a portion of their profits to shareholders. These are primarily mature companies that have already captured the market and have stable cash flows. Dividend payments enable such companies to boost shareholder returns and sustain investor interest in their securities.
However, the largest dividend yield stocks are rarely those of the most successful companies. Above-average yields are usually provided by companies whose business model involves high risks. In 2025, for example, these were predominantly mortgage REITs and BDCs.
Dividends are most often paid in cash. Stock dividends come second. Hybrid and scrip dividends, where investors may receive both cash and new securities, are sometimes encountered. In exceptional cases, companies declare property dividends.
Dividend-paying stocks generate income for investors, even during bear markets and sideways trends. This creates an opportunity to reinvest during periods of low stock prices, thereby increasing the overall return.
These assets are less susceptible to stock market volatility. This primarily applies to companies with a strong track record of increasing dividend payments. The relative price stability of dividend stocks is associated with passive income and high-quality businesses.
The dividend yield calculation is done using the following formula:
Dividend Yield = (Annual Dividend / Current Share Price) x 100%
The formula shows that the market price of a stock affects the outcome. Consequently, the largest dividend yield stocks are often those of companies that have experienced a sharp decline in capitalization.
Top High-Dividend Stocks for 2025
You can use dividend screeners to find the stocks with the highest dividend yields. Such sites not only help you to select the highest dividend stocks, but also offer various other features. They also allow you to sort companies by various metrics. For example, you can sort by payout ratio, dividend CAGR and more.
Below are some examples of the largest dividend yield stocks that have already announced their upcoming dividends at the time of this review:
- Oxford Square Capital Corp. (OXSQ) – 24.42%;
- Whitehorse Finance Inc. (WHF) – 23.05%;
- Horizon Technology Finance Corp. (HRZN) – 21.96%;
- Prospect Capital Corp. (PSEC) – 19.78%;
- Armour Residential REIT Inc. (ARR) – 18.27%.
When it comes to dividend aristocrats, Amcor has the largest dividend stocks. Its dividend yield is 6.42%. Meanwhile, the average for S&P 500 dividend stocks is just 1.2%.
Two Harbors Investment is a prime example of the risk that companies will cut their dividends. In the summer of 2025, the payout was 0.39 dollar for each share, and in the autumn – 0.34 dollars. Prior to this, the company had paid quarterly dividends of $0.45 for two years.
Mesabi Trust is an example of a dividend trap, a phenomenon often associated with the largest dividend yield stocks. Services that report the trailing twelve-month (TTM) dividend yield show that Mesabi Trust’s dividend yield is 22.44%. In February 2025, the company made a one-off payment of $5.95 per share. By way of comparison, the dividend amount in August 2025 was $0.12.
Analyzing Top-Performing Dividend Stocks
A high dividend yield does not guarantee overall profit. Investing in falling stocks can result in a net loss that exceeds the company’s dividend payments.
Investors seeking the highest possible total return may wish to consider the Morningstar Dividend Leaders Index. This index includes the 100 highest-yielding stocks from companies with a stable dividend payment record.
In October 2025, Morningstar lists the best companies such as:
- Invesco (IVZ). The dividend performance over the past 10 years is negative. The 3Y CAGR is 7.02%.
- AES (AES). The 5Y Dividend Growth reached 26.00%.
- Travel + Leisure (TNL). The 3Y CAGR is 16.96%.
It is important to note that these securities are not among the largest dividend stocks. They made the list of highest-yielding payers primarily because of the price appreciation shown over the last 52 weeks.
The price charts for Invesco (IVZ) and Oxford Square Capital Corp. (OXSQ) are shown below. Their respective dividend yields are 3.51% and 24.42%. However, the screenshot shows that REIT shareholders have experienced a negative return over the past year.
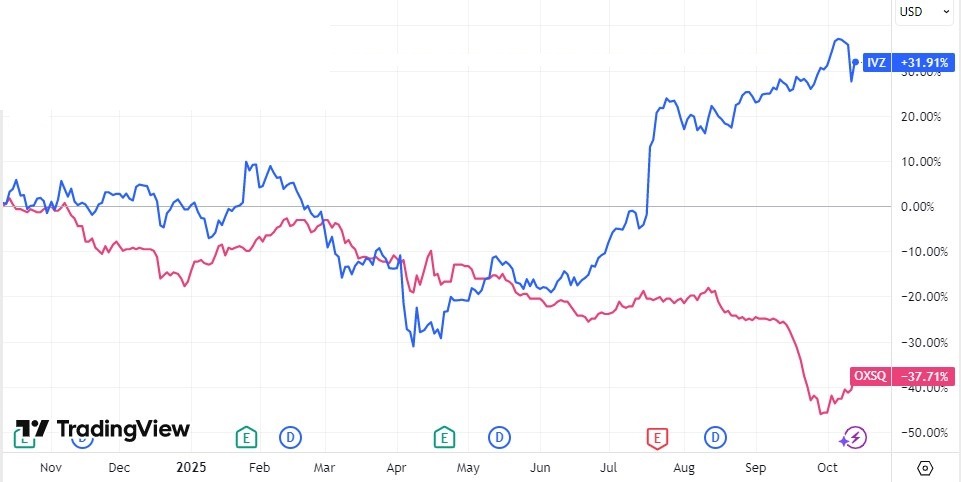
Also, when selecting the largest dividend yield stocks, it is worth paying attention to the ratings from BeatMarket or similar services. These systems typically consider both recent performance and the company’s economic moats.
Risks and Red Flags in High-Dividend Investing
The high dividend yield risks are dividend cuts. There is also the complete cessation of payments. Poor fundamental metrics are a key indicator of troubled companies.
First and foremost, a dividend investor needs to assess the payout ratio. This is calculated by dividing the annual dividend by the annual profit. Values above 80% are a sign of unsustainable dividends.
Given this ratio, there is a risk that the company will be unable to maintain its payment levels if profits decline or expenses rise. However, different norms apply to some sectors. For example, this ratio will be above the market average for REITs due to legislative specifics.
It is important to analyze this warning sign carefully: a sharply falling stock price. It may indicate serious problems within the company. This is often followed by a change in dividend policy.
Evaluating Sustainable Dividend Stocks
When selecting the largest dividend yield stocks as part of a dividend safety analysis, it is advisable to assess the company’s financial health metrics:
- free cash flow coverage ratio;
- the dynamics of the debt-to-equity ratio and analyst credit ratings;
- changes in revenue and profit over the years;
- the length of the dividend streak and consistent payment growth;
- prospects for business expansion and rising costs, such as increasing capex.
An important criterion for assessing dividend sustainability is dividend history. Companies such as Dividend Aristocrats and Dividend Kings have a proven track record of increasing shareholder compensation, even during global crises. This suggests that they are highly likely to maintain stable dividends.
However, past results do not guarantee future returns. Even companies on the Dividend Kings list can experience difficulties and cut their payments.
High-Dividend ETF Investment Strategies
Dividend ETFs are another tool that can provide stable passive income. They offer quick portfolio diversification, ease of trading and relatively low volatility.
Several factors need to be considered when selecting the largest dividend ETF:
- expense ratio;
- the need for sector allocation;
- the fund’s strategy alignment with investment needs.
There are several different types of exchange-traded funds. They differ in terms of their investment strategy and holdings. Broad market funds, for example, differ from funds that specialize in one narrow sector.
The table below provides a dividend ETF comparison.
| Name (Ticker) | Tracked Index | Expense Ratio | Dividend Yield | Investment Focus |
| Vanguard High Dividend Yield ETF (VYM) | FTSE® High Dividend Yield | 0.06% | 2.55% | High current payments |
| Vanguard Dividend Appreciation ETF (VIG) | NASDAQ US Dividend Achievers Select | 0.05% | 1.66% | Stable dividend growth |
| Schwab U.S. Dividend Equity ETF (SCHD) | Dow Jones U.S. Dividend 100 Index | 0.06% | 3.89% | High yield combined with payment stability |
The listed funds are characterized by steady dividends and low volatility. The largest dividend ETF leaders as of mid-October 2025 will be:
- YieldMax Short COIN Option Income Strategy ETF (FIAT) – 284%;
- Proshares UltraShort Ether ETF (ETHD) – 240%;
- Yieldmax MSTR Option Income Strategy ETF (MSTY) – 208%.
These are high-risk funds with extremely unsustainable payment plans. Such assets can be used for ETF diversification as part of an aggressive strategy. However, they are not competitive when it comes to generating a stable stream of income.
International and Sector-Specific Dividend Opportunities
International dividend ETFs provide an opportunity of geographic diversification within a portfolio. These funds also differ in their investment strategies. The following strategies can be identified:
- receiving emerging markets dividends;
- investing in developed markets, excluding the US;
- sector dividend investing, which combines companies from the same sector, but in different countries.
The advantage of geographic diversification is that a downturn in the US stock market can be offset by economic growth in other countries. However, currency considerations must be taken into account when developing a strategy. Exchange rate fluctuations can cancel out the returns earned in foreign markets.
Another important factor for investors in the largest dividend ETF is the tax implications. Many countries impose a withholding tax at source. This can exceed US domestic rates.
Dividend Investment Implementation and Portfolio Construction
A high-dividend stocks portfolio construction involves the following steps:
- Selecting an asset allocation strategy for different sectors and individual companies. Working out how much of each stock is in the portfolio.
- Determining the approach to dividend reinvestment. This can involve manual reinvestment, connecting a brokerage account to a broker’s DRIP program, or participating in individual company DRIPs.
- Developing a portfolio rebalancing procedure.
When developing a strategy, it is necessary to consider the tax implications of receiving dividends.
A portfolio of the largest dividend stocks is rarely considered a fit sole investment. It typically forms part of a broader investment portfolio comprising growth stocks, alternative assets, and defensive components such as bonds and annuities.
Tax Considerations and Advanced Strategies
Simply finding a list of the largest dividend yield stocks is not enough. It is important to keep in mind that tax-efficient investing is a key factor in achieving the best possible outcome.
There are several ways to optimize dividend taxation. For taxable accounts, the simplest option is to receive qualified dividends. These are taxed at long-term capital gains rates (0% – 20%) at federal level. However, this solution is not suitable for most of the largest dividend stocks. REIT payments, for example, cannot be classified as qualified.
Another strategy is tax-loss harvesting. This involves selling assets whose price is below the purchase price. By making a loss on such a transaction, the investor reduces their profit and the amount of tax they owe.
Investors who do not want to spend time studying the intricacies of taxation can use separately managed accounts. These structures mean that the manager will use a strategy tailored to the investor’s individual purposes and tax situation.
Other options include investing in assets that are not subject to taxation. For example, you can use the municipal bonds alternative, which is exempt from federal tax. Another option is buying the largest dividend yield stocks in retirement accounts.
Research Tools and Resources for Dividend Investors
A variety of stock screeners have been developed to help investors build their portfolios. These include fundamental analysis tools. For instance, they allow users to sort companies by debt level, dividend coverage ratio and more. Income investors will also find the dividend tracking and future payment stability forecasting features useful.
The following are examples of stock reliability and dividend research tools and resources:
- The Fidelity screener enables you to sort individual company stocks and ETFs according to a variety of criteria.
- Morningstar analysis. The Morningstar Rating system awards scores from 1 to 5 stars based on a variety of factors.
- The stock analyzer and dividend stock selection from BeatMarket. This service helps you to find new investment ideas with high return potential and reliable payments.
In addition, most companies that provide brokerage account services offer their own screeners to clients.
FAQ – Frequently Asked Questions About Dividend Investing
The ‘Dividend Investing FAQ’ section provides answers to popular dividend yield questions, dividend safety, and dividend timing. It also covers dividend tax questions.
What is considered a “good” dividend yield, and how high is too high?
The competitive dividend yield range depends on the industry in which the company operates. Dividend yield analysis involves comparing the company’s performance with the sector average. Sharp deviations in yield are red flags for an investor. A reasonable dividend yield for US stocks is between 7% and 10%. The high yield risks are future cuts and cancellations of dividends.
How often do companies pay dividends, and when do I receive payments?
The dividend timing depends on the company’s dividend policy. In the US, the most popular dividend payment frequency is quarterly dividends. Information about the dividend payment schedule and the upcoming ex-dividend date can be found on the company’s website and on various financial platforms.
Can companies stop paying dividends, and what are the warning signs?
Investing in the largest dividend stocks carries risks, such as dividend cuts and complete dividend suspension. To identify dividend safety warning signs in good time, it is necessary to conduct a dividend coverage ratio and a payout ratio analysis using cash flow. It is also necessary to take into account financial distress indicators, such as increasing debt and declining profits.
Should I reinvest dividends or take them as cash?
An individual’s personal situation determines their investment strategy choice. If there are no cash flow needs, dividend reinvestment is advisable. This allows you to benefit from the compound growth of capital. The task can be automated and simplified using DRIP programs.
How are dividends taxed, and which account types are most tax-efficient?
Using qualified dividends boosts tax efficiency. These are subject to capital gains tax rates. Dividend taxation can be optimized by using tax-advantaged accounts. For instance, purchasing the largest dividend stocks within an IRA dividend strategy can significantly boost returns thanks to tax deferral.
Article Sources
- NerdWallet (2025). “Dividend Stocks: How To Invest & 7 High-Yield Options for August.” NerdWallet, Inc. Educational content on dividend investing strategies, stock screening criteria, and analysis of high-dividend yield securities including Two Harbors Investment Corp and dividend aristocrats.
- Morningstar, Inc. (2025). “10 Top-Performing Dividend Stocks.” Morningstar Investment Research. Analysis of Morningstar Dividend Leaders Index performance, featuring companies like Invesco (IVZ), AES Corporation, and Travel + Leisure with dividend yield metrics and star ratings.
- ETF Database (2025). “Dividend ETF List – Investment Style Analysis.” VettaFi LLC. Comprehensive database of dividend-focused exchange-traded funds including expense ratios, dividend yields, and holdings analysis for major funds like VYM, VIG, and SCHD.
- Fidelity Investments (2025). “Potentially highest paying dividend stocks in 2025 | High dividend stocks.” Fidelity Brokerage Services LLC. Stock screening methodology for identifying sustainable dividend opportunities, risk assessment frameworks, and analysis of companies like Mesabi Trust and Orchid Island Capital.
- U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (2024). “Investor Bulletin: Dividend-Paying Investments.” SEC Office of Investor Education and Advocacy. Official guidance on dividend taxation, qualified dividend requirements, and investor protection considerations for dividend-focused portfolios.
- Internal Revenue Service (2024). “Publication 550: Investment Income and Expenses.” U.S. Department of Treasury. Tax year 2024 guidelines covering dividend income taxation, qualified vs. non-qualified dividend distinctions, and reporting requirements for dividend distributions.
- Financial Industry Regulatory Authority (2024). “Dividend-Paying Stocks.” FINRA Investor Education Foundation. Educational resource covering dividend payment mechanics, ex-dividend dates, payout ratio analysis, and risk factors associated with high-yield dividend investing strategies.






