- Before you start stock trading, you need to know the answer to the question, ‘What is ex dividend date?’
- The ex-dividend date is an important day for those engaged in dividend investments. Dividend eligibility is tied to this date.
- What is ex dividend date in an investment strategy aimed at receiving dividends? It is the most important of the dividend-related dates. It is the day after which buying a stock no longer entitles you to receive the next dividend payment.
In this article, we will answer the question, ‘What is ex dividend date?’ We will also discuss how this day affects stock trading and explain what happens to stock price on ex dividend date.
Table of Contents
What is a Dividend?
Before examining the question ‘What is ex dividend date?’, it is necessary to define dividends. Dividends are a portion of a company’s profits that are distributed to its shareholders. The main types are:
- Cash dividends. This is the most common option, involving a cash payment to an account, and it is subject to taxation in the year it is received.
- Stock dividends. In this case, the investor receives extra company stocks. Tax liabilities only arise once they are sold.
The type of payment does not affect the answer to the question, ‘What is ex dividend date?’ The meaning of this date remains the same: if you buy on this date, you will not receive the dividends.
Companies pay dividends to boost investor interest and increase shareholder returns. A consistent track record of annual dividend payments and an increasing dividend distribution indicate a company’s financial strength and its management’s confidence in stable cash flows.
Understanding the Ex-Dividend Date
What is ex dividend date when buying stocks? The ex-dividend date (ex-date) is the date from which buying the stock no longer grants dividend eligibility on the next dividend payment date. For example, if the ex-date is October 15th, an investor who purchased the stock on October 14th or earlier will receive the next dividend payment. An investor who makes a transaction on October 15th or later will not.
What is ex dividend date for selling stocks? It is the first trading day on which you can sell a share without losing the right to upcoming dividends. In the above example, a seller who executed a transaction on October 14th would lose the right to the nearest payment. However, if the sale occurred on October 15th or later, the seller retains the right to receive the dividend.
This relates to stock exchange rules and the settlement period. The reason for this is the T+1 settlement cycle. The transfer of ownership of the security does not occur when the order is executed, but one business day later.
Important Dividend Dates: The Complete Timeline
Knowing the answer to the question ‘What is ex dividend date?’ is not enough. The dividend timeline includes three other important dividend dates:
- the announcement date;
- the record date;
- the payment date.
Several weeks usually pass between the declaration date and the ex-dividend date. The record date and the ex-dividend date now coincide. Historically, the ex-dividend date was the trading day before the record date. This was due to the T+2 settlement cycle on some exchanges. However, from 2024 onwards, all exchanges worldwide will operate on a T+1 basis. The period between the ex-date and the payment date is usually a few days to a few weeks.
A different principle for determining the ex-date applies if a cash dividend exceeds 25% of the value of the stock or if the company announces a stock dividend. This will be the first trading day after the payment date. It will no longer coincide with the record date.
Announcement Date (Declaration Date)
The announcement date is when the board of directors publishes information about the amount of dividends to be distributed to shareholders on the upcoming payment date.
A dividend declaration can have a market impact. If the upcoming dividend payment provides a dividend yield that is higher than expected, the stock price rises.
Furthermore, the subsequent dividend dates are also specified on the declaration date.
Record Date
The record date is the date on which a company’s shareholders of record receive dividend eligibility. Ownership verification is based on the company books. This means that only investors who have completed their stock purchase transactions can get the dividend.
What is ex dividend date, and why are two terms used for the same date? In the summer of 2024, the ex-date and the record date began to coincide. Under the T+2 settlement cycle, the ex-dividend date occurred one business day before the record date.
Furthermore, if the company sets the record date for a day when the exchange is not operating, a gap could still theoretically exist between the ex-date and the shareholder records date. For example, if the record date were to be set for Saturday October 11th, the ex-dividend date would be Friday October 10th.
Ex-Dividend Date (Detailed Explanation)
Let’s go back to the question, ‘What is ex dividend date?’ The ex-dividend date is the day on which a stock transaction no longer affects dividend capture. As mentioned above, this is due to settlement rules and the exchange operating on a T+1 basis. Consequently, the stock price adjustment occurs on this day.
When is the ex dividend date? This is announced by the board of directors. Usually, the ex-dividend date is set on the same day as the record date.
Knowing the answer to the question ‘What is ex dividend date?’ is not enough. It is also important to understand how this affects different trading strategies. For example, an investor who wants to receive dividends must consider the timing of their purchase. Similarly, a trader with a short position must consider the additional obligations that arise on the ex-date.
Payment Date
The payment date is the day on which dividend distributions occur. Companies pay a dividend receipt to brokers. The brokers then either make shareholder payments to brokerage accounts or automatically reinvest the dividends.
How Often and When Do Dividends Get Paid?
The dividend frequency is determined by the company’s dividend policy. In the US, quarterly dividends are the most common. These are typical of blue-chip stocks and most large companies. The following dividend schedules are also possible:
- Annual dividends. These are typically found in companies with unstable profits.
- Semi-annual dividends. These are more commonly paid by narrow, sector-specific funds, such as those investing in mining company shares.
- Monthly dividends. These are usually REIT dividends, as well as dividends from other companies with a stable business model.
The Impact of Dividend Dates on Stock Prices
What is ex dividend date, and what stock price impact does it have? By buying shares before the ex-dividend date, a shareholder would be entitled to the dividend and a ‘share’ in the company. However, a transaction on the ex-date or later only grants the right to a ‘share’ in the business.
Therefore, an ex-dividend price drop occurs. Due to market adjustment, the stock valuation decreases by an amount close to the value of the next declared dividend. This process forms the basis of the dividend arbitrage strategy.
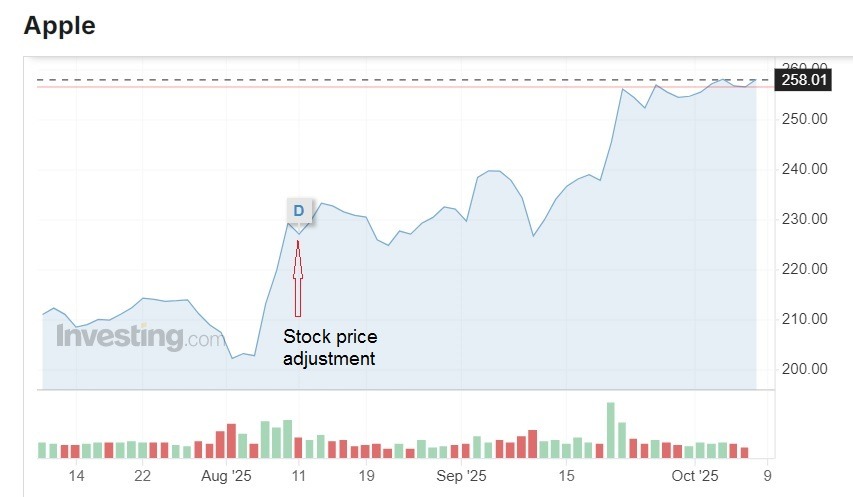
Real-World Example: Apple Dividend Timeline
To answer the question ‘What is ex dividend date?’, let’s provide a dividend example. For a real case study, consider the Apple dividend.
The dividend timeline for the August 14, 2025 payment:
- declaration date – July 31;
- ex-date and a shareholder of record list – August 11;
- payment date – August 14.
The stock price movement on August 11 – from $229.35 to $227.18 or -0.95%.

Strategic Considerations for Investors
There are two global investment strategies related to dividends. The first involves stock purchase, dividend capture and subsequent sale after the price recovers. What is ex dividend date for a dividend hunter? Ex-dividend date is one of the most important dates on which they base the timing of their transactions.
The second strategy is ‘buy and hold’. A person buys stocks and holds them for a long time, regularly receiving income in the process. What is ex dividend date for a long-term passive investor? Essentially, it is a routine date that causes a slight increase in portfolio volatility.
What does ex dividend date mean for the IRS? The dividend timing affects the investor’s tax implications. The ex-date marks the start of the holding period for the stock, which largely determines eligibility for a tax break.
Dividend Metrics and Analysis Tools
For an investor, knowing the answer to the question ‘When is the next dividend payout?’ is not enough. In order to assess the feasibility of buying a dividend stock, it is necessary to consider a number of factors. The key ones are:
- dividend yield;
- dividend payout ratio;
- dividend cover by cash flow.
In addition to dividend analysis, it is important to assess the company’s financial metrics. These include the level of debt, profit and revenue dynamics, and other factors.
Dividend Yield Calculation and Significance
The dividend yield is calculated by dividing the annual dividend by the stock price. There are two approaches to yield calculation:
- a retrospective approach, whereby the annual dividend is determined by adding up all the payments made over the last 12 months;
- a forward-looking approach: to calculate the annual dividend,the last quarterly dividend is multiplied by 4.
What level of income return is considered attractive? The average is taken as the dividend yield of the S&P 500 index, which is currently around 1.2%. However, this answer is influenced by company-specific risks, current market conditions and other factors.
Dividend Payout Ratio Analysis
The payout ratio is an indicator of dividend sustainability. It is calculated by dividing the annual dividend by the annual earnings, and is then expressed as a percentage.
An optimal range is considered to be between 30% and 75%. However, growth companies typically distribute a smaller proportion of their profits to shareholders. By contrast, other types of companies, such as REITs, pay out 80% or more.
For a financial health assessment, earnings coverage is often discussed. This metric is calculated by dividing the EPS by the annual dividend per share.
Advanced Dividend Concepts
For an investor, knowing the answer to the question ‘How does ex dividend date work?’ is not enough. It is also necessary to understand the subtle nuances. For example, it is important not to confuse stock dividends with automatic dividend reinvestment via a DRIP. From the IRS’s perspective, in the latter case, the investor receives cash dividends and must pay tax in the year of the dividend distribution.
An even more complex issue is scrip dividends. When a company announces a dividend of this type, investors can receive stock dividends from the company. However, this type of dividend is taxable in the year it is received.
Another nuance is special dividends. These are paid by a company in the event of a one-time receipt of significant profit. Investors must account for the one-off nature of such payments when assessing future income.
What is ex dividend date in relation to ETF dividends? In this case, it has the same meaning as when investing in individual companies.
Dividend Reinvestment Programs (DRIP)
Dividend reinvestment ensures the compound growth of a portfolio. There are a number of advantages to automatic reinvestment through a DRIP:
- saving time;
- precise adherence to the initial strategy;
- fee-free investing;
- purchasing fractional shares;
- buying shares at a discount.
The last three properties are optional. Some company programs do not allow the purchase of fractional shares and may involve transaction fees. Also, not all companies offer discounts when you enroll in a DRIP.
ETFs and Dividend Distribution
ETF dividends are diversified dividends. The amount received depends on the performance of the many companies whose shares are included in the fund’s net assets.
The distribution schedule largely depends on the type of dividend ETF. For instance, funds that focus on income investing in stocks typically pay out quarterly. Bond funds pay monthly. Funds for shares in gold mining companies pay semi-annually or annually.
Tax Considerations and Dividend Allowances
Earning a profit has tax implications. The rules for calculating dividend income tax and tax-free allowances vary by country. In the UK, for example, dividend allowances exist. If an individual receives less than £500 in dividends, they are not liable for dividend tax.
In the USA, there are tax-advantaged accounts and the concept of ‘qualified dividends’. This type of income is taxed at capital gains rates.
What is ex dividend date for tax purposes? One of the criteria for dividends to be classified as ‘qualified’ is holding the stock for at least 61 days during the 121-day period. This period begins 60 days before the ex-date.
Options Trading and Dividend Risk
From the perspective of options trading, what is ex dividend date? It is a factor of options dividend risk. The associated price adjustment does not happen suddenly. As traders anticipate this event, put options gradually become more expensive and call options become cheaper.
However, there are many other nuances. For example, the early exercise of a call option is probable when it comes to American options. If the option’s extrinsic value is less than the dividend amount, the seller of the contract may receive an options assignment notice.
There are also risks when trying to profit from the put-call parity of European options. When trading options based on dividend stocks, the parity calculation formula must be adjusted.
How to Track and Manage Dividend Information
Proper portfolio management requires timely dividend tracking. How do you find the next ex-dividend date? Each company publishes information about upcoming dividend payments in the investor relations section of its website.
However, tracking many companies separately can be difficult. Therefore, financial platforms publish dividend calendars. These are pages where you can find information about all upcoming ex-dates.
Common Dividend Investment Mistakes to Avoid
Now, let’s consider some key investment errors. The most common are strategy pitfalls. Novice investors, in pursuit of yield, do not pay attention to diversification. Consequently, their portfolio becomes dominated by one or two sectors. This has a negative impact when the phase of the economic cycle changes.
Some investors fall into yield traps. This refers to stocks with a high dividend yield but poor fundamentals and a high risk of dividend cuts.
The second most common type of dividend mistake is a timing mistake. Can you buy on ex dividend date? A trade can be executed on the stock exchange on this date. However, this will not grant the investor the right to upcoming dividends.
Another factor that reduces the investor’s final return is tax inefficiency. One simple way to optimize tax is to hold stocks for long enough to receive qualified dividends. However, this method does not apply to REITs, BDCs, etc.
FAQ Section
The Dividend FAQ section offers investor guidance and answers to common questions about dividend basics.
Do I get a dividend if I buy on the ex-dividend date?
What is ex dividend date? It is the first day on which a stock trades without the dividend. Therefore, ex-dividend date purchases do not grant dividend eligibility. The stock buying timing must be accounted for by the exchange operating on a T+1 basis.
Can I sell a stock on the ex-dividend date and still receive the dividend?
Ex-dividend date selling does not deprive the investor of the right to receive the upcoming dividends. However, it is important to remember that the dividend retention (tax) amount depends on the ownership timing.
How long do I have to own a stock to get the dividend?
The minimum ownership duration to receive dividends is 1 day. You need to buy shares the day before the ex-dividend date and sell them the next day. However, the holding period affects dividend qualification.
Why do stock prices drop on the ex-dividend date?
The ex-dividend price drop is a consequence of market mechanics. The stock price adjustment by the amount of the dividends on the ex-dividend date occurs because purchasing the stock after this date no longer grants the right to the upcoming payment.
What happens if I don’t receive my dividend payment?
If there are dividend problems, investors need to verify whether they were indeed the owner of the stock on the ex-dividend date. If confident in their eligibility for the dividends, they should find their broker’s contact information and inquire about the missing dividends. The broker will help to resolve any payment issues.
Article Sources
- U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (2024). “Investor Bulletin: Ex-Dividend Dates — When Are You Entitled to Stock and Cash Dividends.” SEC.gov, official guidance on dividend eligibility and ex-dividend date mechanics for retail investors.
- NYSE Group (2024). “Listed Company Manual – Section 703.03: Dividend Distributions.” New York Stock Exchange official rules governing ex-dividend date determination and stock price adjustments for listed securities.
- Financial Industry Regulatory Authority (2024). “FINRA Rule 11140: Transactions in Securities ‘Ex-Dividend,’ ‘Ex-Rights’ or ‘Ex-Warrants.’” Official regulatory framework for ex-dividend trading procedures and settlement requirements.
- Chen, H. & Singal, V. (2003). “Role of Speculative Short Sales in Price Formation: The Case of the Weekend Effect.” The Journal of Finance, vol. 58(2), pages 685-705. Academic research on dividend capture strategies and ex-dividend date price behavior.
- Apple Inc. (2024). “Form 8-K Current Report – Dividend Declaration.” Filed with SEC on February 2, 2024, announcing quarterly dividend of $0.24 per share with ex-dividend date February 9, 2024.
- Kalay, A. (1982). “The Ex-Dividend Day Behavior of Stock Prices: A Re-Examination of the Clientele Effect.” The Journal of Finance, vol. 37(4), pages 1059-1070. Seminal academic study on stock price adjustments and trading volume around ex-dividend dates.
- Options Clearing Corporation (2024). “Characteristics and Risks of Standardized Options.” Official disclosure document detailing how dividend payments affect options contracts and early exercise considerations.
- Internal Revenue Service (2024). “Publication 550: Investment Income and Expenses.” U.S. Department of Treasury guidance on tax treatment of dividend income and qualified dividend rates for individual taxpayers.






